Building smarter and more sustainable cities require new ways of thinking from cities and city planners. The whole built environment and different city infrastructures are becoming digital and connected. There will be a vast opportunity to build completely new data ecosystems to create new data-driven smart city services. LuxTurrim5G consortium has released two white papers about designing a smart and sustainable city and creating data marketplace for a smart city. The first one answers the common questions that cities now ponder about sustainability and digitalisation and the second one touches upon the different types of data, stakeholders, and enablers and obstacles for the implementation.
How to design a smart and sustainable city? LuxTurrim5G solution
The aim of smart cities is often seen in improving social, environmental and economic sustainability by utilising modern technologies – providing a low-carbon and environmentally friendly surrounding with maximised citizen well-being and thriving business activities. A smart city is a complex ecosystem of people, policies, services, public and private organisations, technologies etc. (see figure below), all participating in the endeavour of developing an urban environment towards desired outcomes.
Typical smart city ecosystem elements and the three dimensions of sustainability.
To enable the creation of new 5G and data driven smart city services, cities need to
Understand the needed services for the target location
Plan and support the building of the smart infrastructure
Establish a local entity to build, host and operate the smart infrastructure - including local 5G frequencies - and data marketplace which facilitates the developer community and access to the smart infrastructure
Data markets in future smart cities
The evolving smart city infrastructures provide a base for new smart city data markets and new possibilities and incentives for data supply and use. To utilise smart city data maximally, we need markets where citizens, authorities and private companies can sell and buy data, process the data and create added-value data products from existing and new data and develop solutions for data use. In addition to earning direct profits from data sales, data trade can provide other benefits for data sellers, e.g., new partners, new interests in the company's main products, new kinds of business activities and new customers, as a result of data-based solutions.
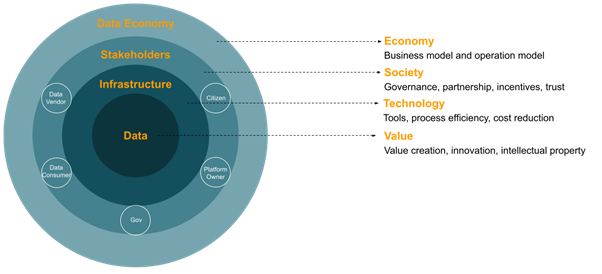
Conceptual model for smart city data economy.
In the white paper, the key questions related to data business in smart cities are discussed; a model for local 5G data marketplaces and a four-level categorisation for sellable data products; and the benefits, obstacles and enablers of data business in the future local data marketplaces are presented.
How to apply smart city solutions
Smart city data economy creates new incentives for the citizens, authorities, and companies to share data and to act as data buyers and sellers. The data buyers can develop solutions for data use or process the data and sell the processed data to other actors on the market (see figure below).
The connectivity and data platforms enable new value adding services and products that would not be commercially attractive without the digital backbone. Standardized data flow and marketplace allow low effort service development and creation of secure solutions between the city and the citizens.
Data marketplace unites the various data stream, data sellers and buyers, and data driven solutions.
LuxTurrim5G ecosystem provides the digital backbone for building smart and sustainable cities. The key elements, modular 5G/IoT smart poles, exist as a pre-commercial product family serving the various needs of cities. Several digital services related e.g. to public safety, last-mile logistics, autonomous transport and healthy living have been piloted and prepared for commercialization. Together with a secured local data platform this all provides a holistic solution for cities, helping them to turn smart and sustainable and to be ready for new unforeseen digital service needs.
Read more